The hardest language in the world can depend on the person learning it, especially their native language. However, some languages are generally seen as more difficult than others. Mandarin Chinese, Arabic, Japanese, and Korean are often ranked as the hardest to learn. This is because they have complex writing systems, difficult grammar, and unusual pronunciation. For example, Mandarin Chinese uses tones that can change the meaning of a word and has thousands of characters to memorize. Arabic is written from right to left and has unique grammar rules. Japanese and Korean also have difficult scripts and formal language levels.
Many experts say Mandarin Chinese is the most difficult language in the world, especially for English speakers. This is because it has tonal sounds, uncommon expressions, and almost no words that are similar to English. Around 6,900 languages are spoken worldwide, with Asia having the most over 2,000 languages while Europe has about 230. Other languages like Finnish and Cantonese are also very hard to learn because of their tricky grammar and many word forms. Overall, these languages are considered the most challenging in the world.
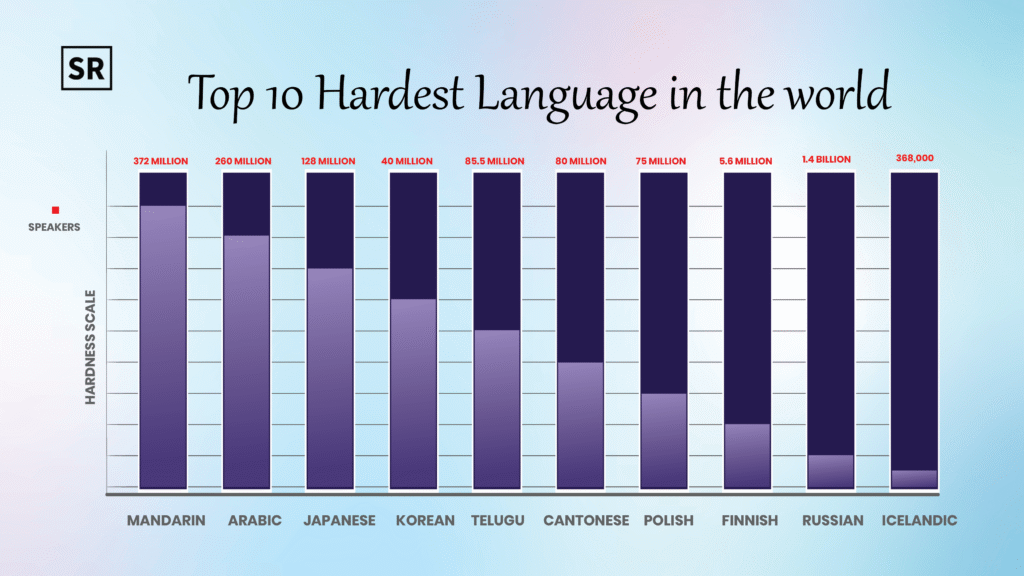
Top 10 Hardest Languages in the World
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU

Fresnillo Share Price Prediction (2025–2030): Expert Analysis & Predictions
Team SR
May 27, 2025
Hardest Languages in the World: In this part, we will talk about the 10 most difficult languages to learn.
| Language | Why It Is Difficult |
| Mandarin | Uses tones (same word can mean different things), thousands of characters to remember |
| Arabic | It is written right-to-left, usually leaves out short vowels (so you must guess the pronunciation), and has many very different dialects. |
| Japanese | You must know three alphabets (hiragana, katakana, kanji) and use special words and endings depending on how polite you want to sound. |
| Korean | Unique script (Hangul), verbs change based on mood and respect |
| Telugu | Its script has many combined letters (conjuncts) and sentences are built Subject-Object-Verb, which is the opposite of English. |
| Cantonese | More tones than Mandarin, grammar is different |
| Polish | Has 7 cases (word forms), hard to pronounce words |
| Finnish | 15 different noun forms, verbs change a lot |
| Russian | Uses Cyrillic script, grammar changes a lot with word endings |
| Icelandic | Has grammatical genders, cases, and difficult sentence structure |
Mandarin
Mandarin is the official language of China and one of the most spoken languages in the world. It belongs to the Sino-Tibetan language family. Mandarin is a tonal language, meaning the tone in which a word is spoken can change its meaning. It uses thousands of unique characters instead of an alphabet, which makes reading and writing challenging for learners. Despite its difficulty, Mandarin is becoming increasingly important globally due to China’s growing influence in the world.
- Mandarin is the official language of China.
- It is the most widely spoken language in the world.
- It belongs to the Sino-Tibetan language family.
- Mandarin is a tonal language changing the tone changes the meaning of a word.
- It uses characters, not an alphabet, with thousands to learn.
- Reading and writing can be difficult for new learners.
- It is becoming more important globally due to China’s influence.
Arabic
Arabic is a widely spoken language in the Middle East and North Africa. It is the official language of over 20 countries and one of the oldest languages in the world. Arabic has a unique script written from right to left and includes many sounds that are difficult for non-native speakers to pronounce. There are many dialects of Arabic, which can vary greatly from region to region. Modern Standard Arabic is used in formal settings, media, and education, while spoken Arabic differs in everyday conversation.
- Arabic is spoken in the Middle East and North Africa.
- It is the official language of more than 20 countries.
- Arabic is one of the oldest and richest languages in history.
- It is written from right to left using a unique script.
- It has several sounds that are hard for non-native speakers to pronounce.
- There are many regional dialects, which can differ a lot.
- Modern Standard Arabic is used in schools, media, and formal writing.
- Spoken Arabic changes based on the country or region.
Japanese
Japanese is the official language of Japan and is spoken by over 125 million people. It is known for its complex writing system, which combines three scripts: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji (characters borrowed from Chinese). The grammar structure is very different from English, and it uses polite forms of speech depending on social status and situation. Japanese pronunciation is relatively simple, but reading and writing can be challenging due to the large number of characters and the use of multiple scripts.
- Japanese is the official language of Japan.
- It is spoken by over 125 million people.
- The language uses three writing systems: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji.
- Kanji characters come from Chinese and can be difficult to memorize.
- Grammar is very different from English, with strict sentence structure.
- The language includes polite and formal speech levels based on social context.
- Pronunciation is relatively easy, but reading and writing can be hard.
Korean
Korean is the official language of South Korea and North Korea. It has over 75 million speakers worldwide. The Korean writing system, called Hangul, is unique and was created in the 15th century. Hangul is known for being logical and easy to learn compared to other writing systems. Korean grammar is different from English, with subject-object-verb sentence order and the use of honorifics to show respect. While the pronunciation is generally regular, some sounds can be tricky for non-native speakers.
- Korean is the official language of South Korea and North Korea.
- Spoken by over 75 million people worldwide.
- The writing system is called Hangul, created in the 15th century.
- Hangul is known for being simple, logical, and easy to learn.
- Korean grammar uses subject-object-verb word order.
- It includes honorifics to show respect based on age or status.
- Pronunciation is regular but may have some difficult sounds for learners.
Telugu
Telugu is a Dravidian language spoken mainly in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. It is one of the 22 official languages of India and one of the most spoken languages in the country. Telugu has a rich literary history and is known for its classical poetry and expressive script. The script is rounded and elegant, derived from the Brahmi script. Telugu grammar is complex, with a subject-object-verb word order and various verb forms. It is also known as "The Italian of the East" because of its musical and vowel-ending words.
- Telugu is a Dravidian language spoken mainly in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, India.
- It is one of the 22 official languages of India.
- Telugu has a rich literary and cultural history.
- The script is rounded and artistic, derived from the ancient Brahmi script.
- Known for its melodic sound, often called "The Italian of the East."
- Follows subject-object-verb sentence structure.
- Grammar is detailed, with various verb forms and honorifics.
- Widely spoken by millions of people in India and abroad.
Cantonese
Cantonese is a Chinese language spoken mainly in Hong Kong, Macau, and the Guangdong province of China. It is also widely spoken in Chinese communities around the world. Cantonese is known for its complex tones it has six to nine tones, depending on how they are counted. This means the same syllable can have many different meanings based on tone. Unlike Mandarin, Cantonese is not commonly written in everyday use, though written Chinese is generally understood. The language is rich in expressions and culture but is considered difficult to learn due to its tones and pronunciation.
- Cantonese is spoken in Hong Kong, Macau, and Guangdong province.
- Also spoken in many Chinese communities worldwide.
- It is a tonal language with 6 to 9 tones, making pronunciation challenging.
- The same syllable can have different meanings depending on the tone.
- Uses traditional Chinese characters in writing.
- Different from Mandarin in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar.
- Not commonly used for everyday writing, but spoken widely.
- Known for its rich culture and expressions, especially in films and music.
Polish
Polish is the official language of Poland and is spoken by over 40 million people worldwide. It belongs to the West Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family, closely related to Czech and Slovak. Polish uses the Latin alphabet but includes special letters with accents, making pronunciation and spelling difficult for learners. The grammar is complex, with seven cases, gendered nouns and verb conjugations. Despite its challenges, Polish has a rich literary and cultural history and is an important language in Central Europe.
- Polish is the official language of Poland.
- Spoken by over 40 million people worldwide.
- Belongs to the West Slavic group (related to Czech and Slovak).
- Uses the Latin alphabet with special accented letters.
- Has complex grammar with 7 cases and gendered nouns.
- Pronunciation and spelling can be difficult for new learners.
- Rich in literature, culture, and history.
- An important language in Central and Eastern Europe.
Finnish
Finnish is the official language of Finland and one of the two official languages of the European Union from Finland, along with Swedish. It belongs to the Uralic language family, which is very different from most European languages that come from the Indo-European family. Finnish has a unique structure, with long words, vowel harmony, and 15 grammatical cases. It has a consistent pronunciation and spelling system, which makes reading easier but mastering the grammar can be quite difficult. Despite its challenges, Finnish is known for its rich folklore, poetic expressions and logical structure.
- Finnish is the official language of Finland.
- Also one of the official EU languages from Finland (along with Swedish).
- Belongs to the Uralic language family, not related to most European languages.
- Known for its 15 grammatical cases, making grammar complex.
- Uses vowel harmony and long compound words.
- Pronunciation and spelling are regular and consistent.
- Difficult to learn due to complex grammar, but logical in structure.
- Rich in folklore, nature-inspired vocabulary, and poetic expressions.
Russian
Russian is the official language of Russia and is widely spoken across Eastern Europe and Central Asia. It belongs to the East Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family. Russian uses the Cyrillic alphabet, which is different from the Latin alphabet used in English. The language has complex grammar with six cases, verb conjugations, and gendered nouns. Russian pronunciation can be challenging, especially with its hard and soft consonants. It is an important language for culture, science, and politics in the region.
- Russian is the official language of Russia.
- Spoken widely in Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
- Part of the East Slavic branch of the Indo-European family.
- Uses the Cyrillic alphabet.
- Grammar includes 6 cases, verb conjugations, and gendered nouns.
- Pronunciation involves hard and soft consonants, which can be tricky.
- Important for culture, science, and politics in the region.
- Spoken by over 150 million native speakers worldwide.
Icelandic
Icelandic is the official language of Iceland and is spoken by about 350,000 people. It is a North Germanic language closely related to Old Norse, the language of the Vikings. Icelandic has changed very little over the centuries, which means modern Icelanders can still read ancient texts with relative ease. The language has a complex grammar system with four cases and three genders. Icelandic pronunciation and spelling can be difficult for learners, but its rich literary tradition and preserved history make it unique among European languages.
- Icelandic is the official language of Iceland.
- Spoken by around 350,000 people.
- A North Germanic language closely related to Old Norse.
- Has changed very little over centuries, allowing modern speakers to read old texts.
- Features complex grammar with four cases and three genders.
- Pronunciation and spelling can be challenging for learners.
- Known for its rich literary tradition and historical preservation.
- Unique among European languages due to its close link to Viking heritage.
What is FSI Language Difficulty?
FSI Language Difficulty refers to a classification system created by the Foreign Service Institute (FSI) of the U.S. Department of State. It measures how hard it is for native English speakers to learn different foreign languages based on the average time it takes to reach proficiency.
Key points about FSI Language Difficulty :
The FSI groups languages into categories or "difficulty levels" based on the approximate number of classroom hours needed for an English speaker to become proficient.
- Category I (easiest): Languages like Spanish and French, which usually take about 600-750 hours.
- Category II & III: Medium difficulty languages, such as Indonesian or Russian, taking around 900-1100 hours.
- Category IV (hardest): Languages like Arabic, Chinese, Japanese, and Korean, which can require 2200+ hours or more to learn well.
- The rating considers grammar, writing system, pronunciation, and cultural differences.
The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) Language Categories
The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) groups languages based on how hard they are for English speakers to learn :
Category I – Easiest Languages
- Take about 600 to 750 hours to learn.
- Examples: Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish.
- These languages are similar to English in alphabet, grammar and words.
Category II – Somewhat Harder Languages
- Take about 900 hours to learn.
- Example: German.
- Grammar and pronunciation are a bit more difficult than Category I but still okay.
Category III – More Difficult Languages
- Take about 1100 hours to learn.
- Examples: Indonesian, Swahili, Russian, Hindi, Turkish and Hebrew.
- These languages have different grammar, words or writing systems from English.
Category IV – Hardest Languages
- Take about 2200 hours or more to learn.
- Examples: Arabic, Chinese (Mandarin and Cantonese), Japanese and Korean.
- Very different grammar, writing, tones and culture from English.
Conclusion
Learning a new language can be exciting but also challenging especially if it is very different from your native language. Some languages, like Spanish or French are easier for English speakers because they share similar grammar and vocabulary. Others, like Arabic, Mandarin, or Japanese, are much harder due to complex writing systems, tones, or grammar rules. The difficulty of a language depends on many factors such as pronunciation, script, sentence structure and cultural differences. While some languages take more time and effort to learn, they also offer rich history, culture, and new ways of thinking. No matter the difficulty, learning any language is a valuable and rewarding experience.


 Follow us
Follow us Follow us
Follow us













